Roots blower for sewage treatment It is a positive displacement fan, with impeller end face, fan front and rear end covers. The principle is a rotary compressor that uses two blade rotors to make relative movement in the cylinder to compress and transport gas. The blower is simple in structure and easy to manufacture. It is widely used in aquaculture oxygenation, sewage treatment aeration, cement transmission, and more suitable for gas transmission and pressurization systems in low pressure occasions, and can also be used as a vacuum pump.
form:
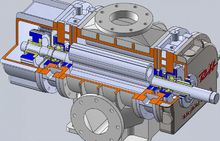
Roots blower is composed of five parts: casing, wallboard, impeller, oil tank and muffler.
Casing: mainly used for supporting (wallboard, impeller, muffler) and fixing.
Wall plate: mainly used to connect the casing and the impeller, support the rotation of the impeller, and play the role of end sealing.
Impeller: it is the rotating part of Roots blower, which is divided into two leaves and three leaves. However, due to the advantages of three leaves, such as less air pulsation, less noise, and more stable operation than two leaves, it has gradually replaced the two leaves Roots blower.
Oil tank: mainly used to store lubricating oil used to lubricate gears and bearings.
Muffler: It is used to reduce the noise caused by air flow pulsation during the inlet and outlet of Roots blower.
Principle:
Roots blower is a type of volumetric fan. There are two three blade impellers that rotate relatively in the space sealed by the casing and wall plate. Since each impeller is involute or the envelope of the epicycloid, the three blades of each impeller are identical, and the two impellers are identical, which greatly reduces the processing difficulty. Numerical control equipment is used during impeller processing to ensure that a certain minimum clearance can be maintained no matter where the two impellers rotate, under the condition that the center distance between the two impellers is constant, so as to ensure that the gas leakage is within the allowable range.
The two impellers rotate in opposite directions. Because the clearance between impellers and impellers, between impellers and casings, and between impellers and wallboards is very small, a vacuum state is formed at the air inlet. The air enters the air inlet chamber under the action of atmospheric pressure. Then, two of the blades of each impeller form a sealed chamber with wallboards and casings, The sealing chamber formed by two blades is constantly taken to the exhaust chamber, and because the impellers in the exhaust chamber are meshed with each other, the air between the two blades is squeezed out. In this way, the air is continuously transmitted from the air inlet to the air outlet, which is the whole working process of Roots blower.


